Decoding the Language of AI - A Beginner's Journey into Large Language Models
Imagine teaching a computer to understand and even speak our language. This might sound like a plot from a science fiction novel, but it's a reality we're living today, thanks to a technology called Large Language Models (LLMs). These sophisticated programs, such as the one behind your digital assistant or the chatbot on your favourite shopping site, are transforming how machines interpret and generate human-like text. But how does this technology work? How can a machine grasp the nuances of our language and respond in kind? In this beginner's guide, we'll embark on an intriguing journey to understand the basics of LLMs – breaking down complex AI concepts into simple, digestible bits. From the way these models dissect language to how they predict the most appropriate responses, we'll explore the fascinating world of AI language understanding, one step at a time.
What Are Tokens?
In the realm of Large Language Models, a 'token' is a fundamental concept, acting as the basic unit of text that the model processes. To understand tokens, think of how we read a sentence. We don't just see a string of characters; instead, we instinctively break it down into smaller units like words and punctuation. Tokens serve a similar purpose in LLMs.
These tokens can be entire words, parts of words (like '-ing' in 'running'), or even punctuation marks (like a full stop). This breakdown helps the AI model to analyse the text in chunks, making it easier to understand the structure and meaning of sentences. By processing language in tokens, LLMs mimic the human approach to reading, allowing them to grasp and generate language in a way that feels surprisingly natural.
Tokenisation: Splitting Text into Tokens
The process of breaking down text into tokens is known as 'tokenisation'. It's akin to dissecting a sentence into its constituent parts to better understand its meaning. When an LLM encounters a block of text, it doesn't see it as a whole. Instead, it uses tokenisation to split the text into manageable pieces – the tokens.
For instance, the sentence "The quick brown fox" would be tokenised into separate units like 'The', 'quick', 'brown', and 'fox'. This process allows the LLM to analyse each part of the sentence, understanding its structure and context. Tokenisation is crucial because it turns complex, varied text into a uniform format that the LLM can process and analyse more effectively. It's the first step in transforming human language into something an AI model can understand and work with.
You can see how OpenAI sees tokens here: https://platform.openai.com/tokenizer
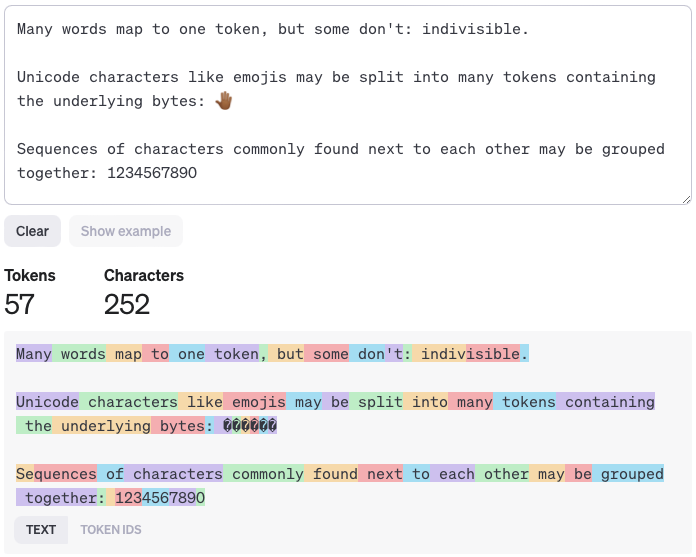
Generating Responses: Understanding Tokens, Token IDs, and Probability
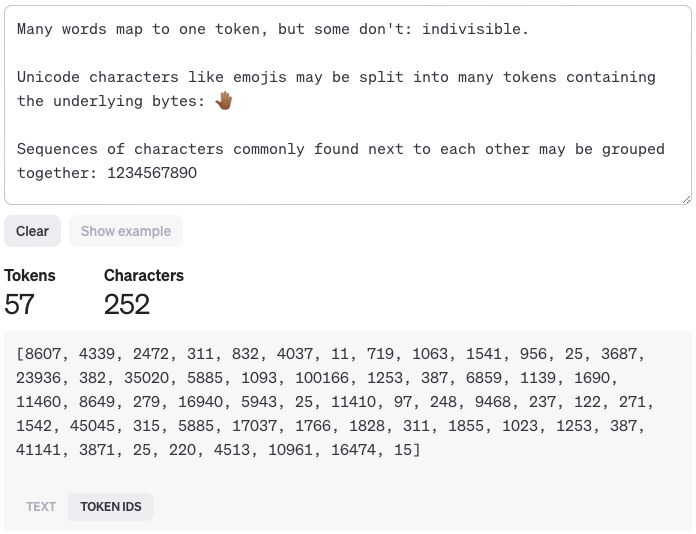
After an LLM tokenises text, it generates responses using a combination of tokens, token IDs, and probability. Each token is assigned a unique identifier, known as a Token ID. This ID is crucial as it helps the model distinguish between different tokens, even if they are the same word. For instance, the word 'bank' would have different Token IDs based on its context (river bank vs. financial bank).
For example, let's consider the sentence, "The cat sat on the mat." Each word (token) here is converted into a numerical ID - 'The' might be 102, 'cat' 205, and so on. When generating a response, the LLM doesn't just look at the words; it analyses these Token IDs, using statistical probabilities to predict the next most likely Token ID in the sequence.
So, if our sentence ends with "The cat sat on the...", the model evaluates the statistical likelihood of each possible next word (Token ID) based on its training. If in its vast dataset 'mat' often follows 'The cat sat on the', the Token ID for 'mat' will have a higher probability, and the model is more likely to select it as the next word. This method of using Token IDs and statistical analysis enables the LLM to generate responses that are not only contextually appropriate but also incredibly varied and nuanced, depending on the training and the specific tokens involved.
Hopefully this article has shed some light on how LLMs work and shown that they are not some sentient being that has a form on consciousness! It is a highly advanced prediction machine based on assigning chunks of text with numerical values - basically, it's the next generation probability calculator. A tool that will change the world and the way we work with an impact as large as the birth of the internet.
❤️ Enjoyed this article?
Forward to a friend and let them know where they can subscribe (hint: it's here).
